kenya
the biggest and most advanced economy in east & central africa
Kenya is the largest and the most advanced economy in East and Central Africa with strong growth prospects, supported by an emerging urban middle class and an increasing appetite for high-value goods and services. The government of Kenya is generally investment friendly and has enacted several regulatory reforms to simplify both foreign and local investment, including the creation of an export processing zone.
Kenya is a very young country with more than 60% of the population aged below
25 years. Kenya has a diverse population that includes most major ethno-racial and linguistic groups found in Africa. Nairobi is the capital and largest city of Kenya. With thousands of Kenyan businesses and over 100 major international companies and organizations, it is an established hub for business and culture.
Indians who are locally called as the 'Muhindis' are an integral part of Kenya. They are a major force in Kenyan economy and play an important role in business, judiciary, medical and academics. Indian enterprises are one of the largest employers in the Kenyan private sector. Many key businesses in Kenya are owned by people of Indian origin which include sectors such as manufacturing, agriculture, food processing, fisheries, transportation and infrastructure development, banking, finance, hotel and tourism.

INDIA-KENYA BILATERAL RELATIONS
India and Kenya are maritime neighbours. The contemporary ties between India and Kenya have now evolved into a robust and multi-faceted partnership, marked by regular high-level visits, increasing trade and investment, as well as extensive people to people contacts. India was Kenya's largest trading partner in 2014-15 with bilateral trade of US$ 4.235 billion. In 2017-18, bilateral trade was US$ 2.05 billion and for the period April to August 2018, bilateral trade was US$ 1.062 billion. Main Indian exports to Kenya include petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, steel products, machinery, yarn, vehicles and power transmission equipment. Main Kenyan exports to India include soda ash, vegetables, tea, leather and metal scrap
According to the Kenya Investment Authority (KenInvest), India is the second largest investor in Kenya. Over 60 major Indian companies have invested in various sectors including manufacturing, real estate, pharmaceuticals, telecom, IT & ITES, banking and agro-based industries. Indian investments have resulted in creation of thousands of direct jobs to Kenyans. Indian pharmaceutical companies have a substantial presence in Kenya. In 2017, Kenya ranked 92nd in the World Bank ease of doing business rating from 113rd in 2016 (of 190 countries).
Kenya Vision 2030 is the country's development blueprint which was launched in 2008. The long-term goals of this vision are to create a prosperous and globally competitive nation with a high quality of life by the year 2030. To do this, it aims to transform Kenyan industry all the while creating a clean and secure environment. The vision is separated into three different pillars: economic, social, and political governance.
THE BIGGEST SHOWCASE OF INDIAN PRODUCTS AND SERVICES IN KENYA
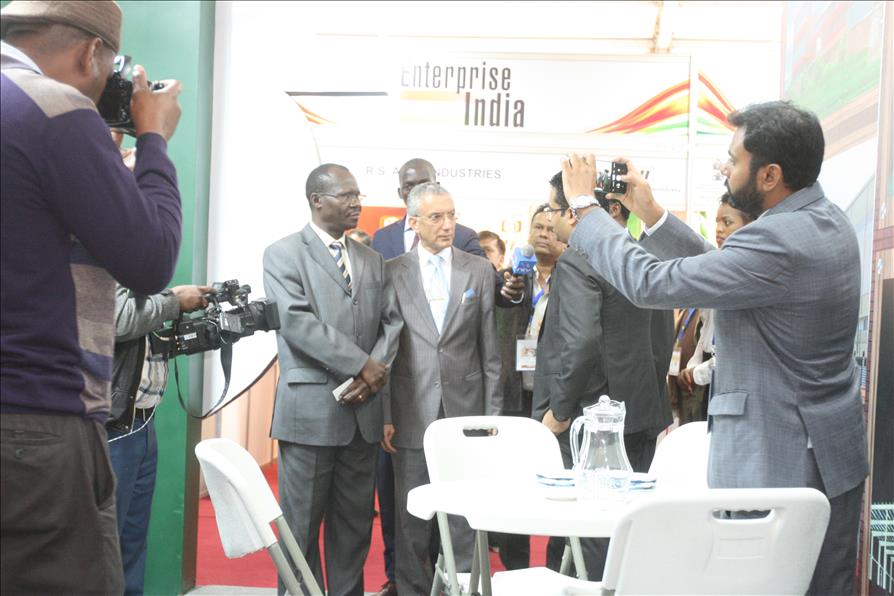
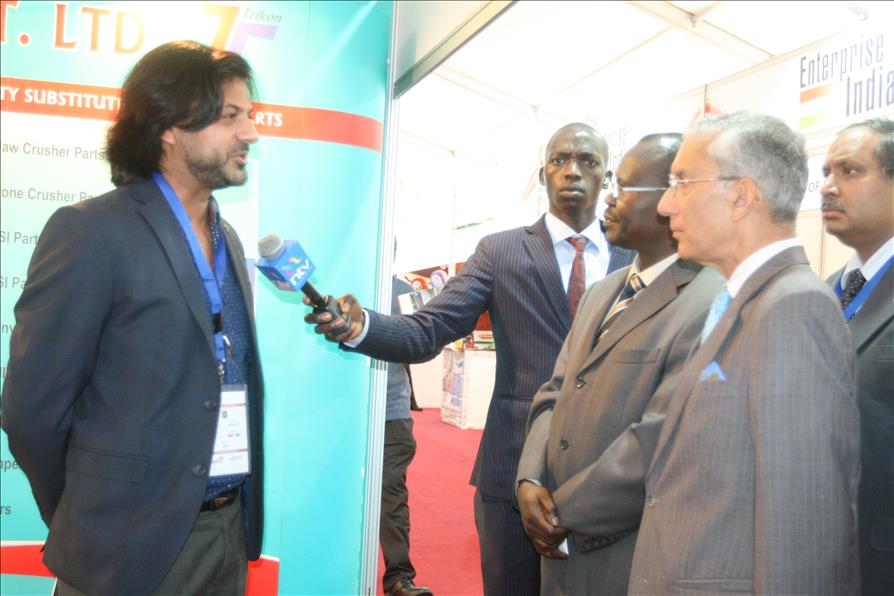
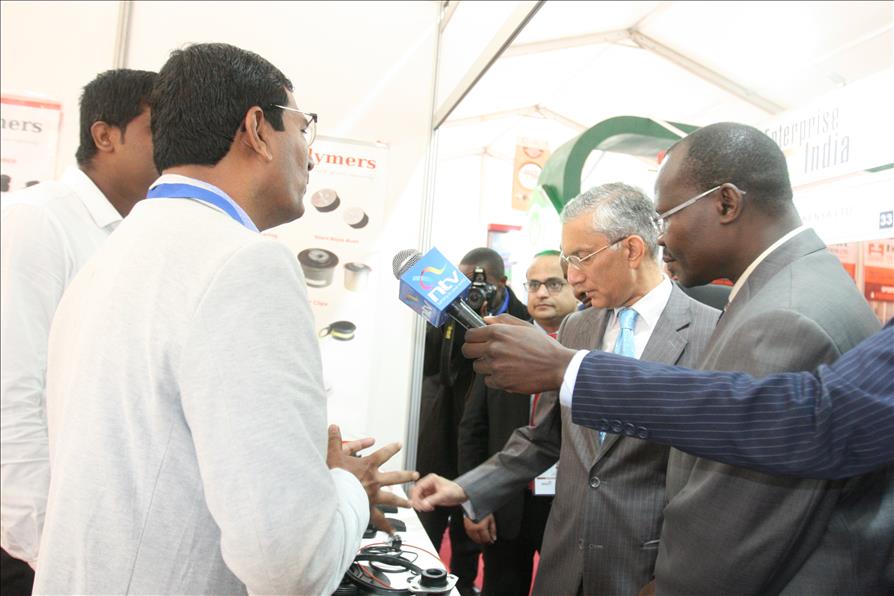
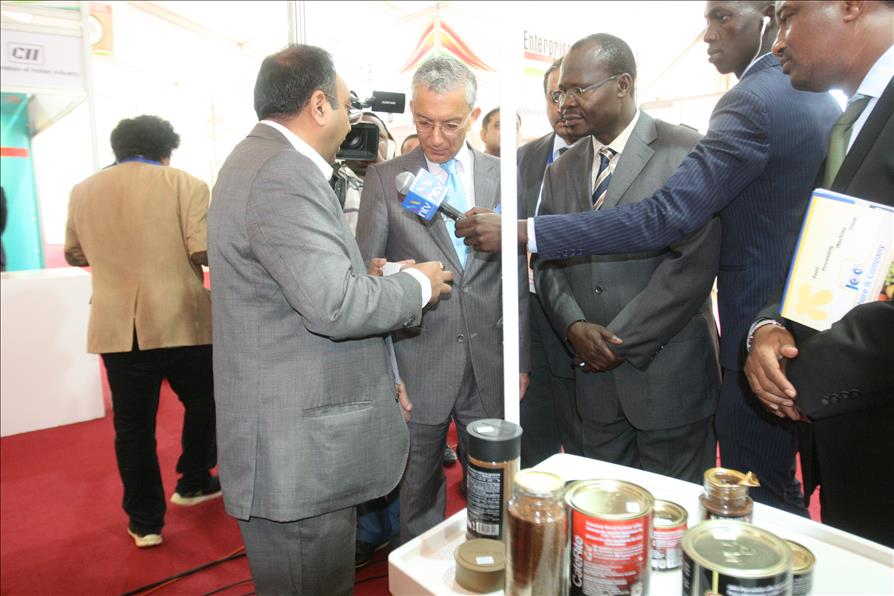
Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), in association with the High Commission of India, Nairobi, Kenya along with the support of Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India is organising “Enterprise India” Show (Nairobi, Kenya) to promote ‘Brand India’ and the Indian industry overseas, especially in developing countries having demand for Indian products, services and technologies.
The primary objective of the “Enterprise India” show is to enhance bilateral trade and investment between India & Kenya and create awareness on the business opportunities available for both sides. The event would provide a platform for business meetings, international conference and seminar, business networking, technology assessment, strategic partnership, vendor development and will be attended by visitors from the local community in Kenya and industry professionals across Africa.
Key Components

3 DAY EXHIBITION

INAUGURAL CEREMONY

B2B MEETINGS WITH LOCAL BUYERS

GOVERNMENT & TRADE DELEGATION

FOCUSED SEMINAR / CONFERENCE
NETWORKING & KNOWLEDGE SHARING
EXHIBITOR PROFILE
- Automobile Parts
- Commercial Vehicles
- Cutting Tools & Hand Tools
- Electric Motors & Generators
- Batteries & Invertors
- All types of Wires and Cables
- Transformers & Switchgears
- Pumps, Compressors & Diesel Engines
- Machine Tools & Accessories
- Agro & Food Processing
- Infrastructure & Urban Development
- Construction Machinery
- Tractors, Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Sanitary & Hardware
- Industrial Automation & Robotics
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Petroleum Products
- Chemicals & Allied Products
- Machinery for Mining
- Heavy Engineering Machinery
- Industrial Castings & Forgings
- Steel Pipes / Tubes & Fittings / Flanges
- Lifting, Handling Equipment & Parts
- Pharmaceuticals Machinery & Equipment
- Medical & Health Care
- Packaging Machines, Equipment & Material
- Lighting & Power Controls
- Water & Waste Management
- Rubber & Plastics
- Machines & Equipment for Printing of Packaging Material
- Food Technology
- Refrigeration & Air-conditioning
- Electricals
- Tourism & Hospitality
- IT & ITES
- Telecom
- Education
- Banking & Financial Services
- Consumer Durables
VISITOR PROFILE
- CEO's / Decision Makers
- Department Heads & Managers
- Buyers & Sourcing Personnel
- Ministerial & Trade Delegation
- Entrepreneurs
- Importers & Agents
- Distributors & Dealers
- Retailers & Traders
- Contractors & Consultants
- Government Officials
- Institutional Investors
- Technical Experts
- Industrial Chambers & Associations
- Academia
- Media



















































